Are vegetable and seed oils “poisonous”?!
From TikTok to bestseller lists, vegetable oils—a.ok.a. “seed oils”—are a large matter at this time.
To be honest, other people have debated the deserves of vegetable oils courting again to once they first entered {the marketplace}.
Extra just lately, then again, with the arrival of the carnivore vitamin, vegetable oil hate has roared again into the socials. Possibly you’ve come throughout posts that refer to those cooking oils as “poisonous sludge,” “motor oil,” “the hateful 8,” and “the most important reason for persistent illness that no person is aware of about.”
The anti-vegetable oil common sense is going one thing like this…
Animal fat were with people for 1000’s of years. Vegetable fat, however, had been invented all through the ultimate century when profit-seeking firms sought after to give you the chance to promote cheap-to-grow meals to unsuspecting customers.
Any other argument: Like margarine, vegetable oils had been advertised as more fit possible choices for butter, and but, folks argue, those oils are worse than butter, elevating your possibility for weight problems, nervousness, melancholy, ulcerative colitis, and extra.
By contrast to the above line of idea, different mavens will let you know that vegetable oils are risk free, doubtlessly even health-promoting—and completely higher than butter.
So, who’s proper?
Like such a lot of diet subjects, in actual fact too nuanced to suit on a meme.
On this tale, we’ll will let you type the science from the pseudoscience so you’ll be able to make knowledgeable choices concerning the oils you select to incorporate on your vitamin.
What are vegetable oils?
Also known as “seed oils,” vegetable oils get started, as you could suspect, from the seed of a plant. The commonest ones you’ll in finding in a normal grocery aisle come with:
Canola oil
Corn oil
Safflower oil
Sesame oil
Sunflower oil
Soybean oil
Grapeseed oil
Via the best way, if you’re feeling like there’s a number of oils lacking from that record, it’s most likely as a result of the ones oils come from non-seed vegetation (akin to olive, avocado, palm, or coconut oil, which all come from culmination, and aren’t regarded as vegetable or seed oils).
How are vegetable oils processed?
Non-vegetable oils—akin to olive and avocado oil—are derived from naturally fatty meals. If truth be told, olives are so oily that you should theoretically make your individual olive oil at domestic. (Simply Google “find out how to make olive oil from scratch,” and also you’ll in finding quite a few movies strolling you in the course of the steps.)
The similar can’t be mentioned of maximum vegetable oils, which most commonly come from meals with a somewhat tiny fats content material to start with.
Living proof: A cup of inexperienced olives comprises about 20 grams of fats,1 while a cup of corn has 2 grams.2
Consequently, producers should use an in depth multi-step procedure to extract this small quantity of oil from those non-oily meals. Those steps come with:
Crushing: A device makes use of excessive power to press oil from the seeds.
Refining: The seeds are heated with a solvent, akin to hexane, to extract extra oil.
Deodorizing: To create a impartial style and take away undesirable compounds, the extracted oil is then cooked at 400 F (204 C) for a number of hours.
All the way through this procedure, health-promoting polyphenols and different stabilizing vitamins are misplaced, and small quantities of unsaturated fat are reworked into trans fatty acids (also known as in part hydrogenated fats).
(Attention-grabbing truth: This additionally occurs all through deep frying. When vegetable oils sizzle in a cafe’s deep fryer for hours, the trans fats content material of the oil will increase.)
To name those processed oils “poisonous” could be an exaggeration. Then again, diet scientists normally agree that folks will have to keep away from trans fat within the vitamin, and in 2018, the Meals and Drug Management banned producers from including trans fat to processed meals.3 4
What cooking oils will have to you devour?
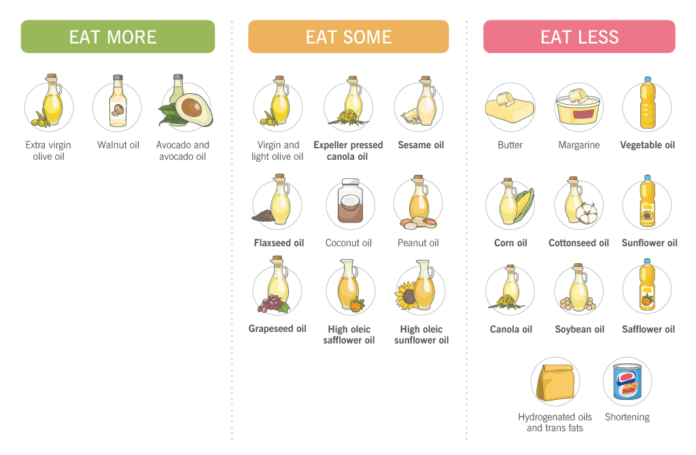
At PN, we’ve created a number of visible guides folks can use to make knowledgeable choices about what to devour.
(We’ve additionally created a buying groceries record, which you or your shoppers can print out and take to the grocer. Test it out: Healthy Fats Shopping List)
In those guides, we’ve positioned a couple of vegetable oils—expeller-pressed canola oil, high-oleic sunflower, and safflower oils—within the “Devour Some” phase. For us, “devour some” is in a different way of claiming that those meals will neither strengthen fitness nor hurt fitness—when fed on in affordable quantities. In some instances, like within the instance of darkish chocolate, when fed on in small quantities, they could even strengthen fitness.
The remainder of the vegetable oils, at the side of butter and different saturated fat, fall into the “Devour Much less” class, as the picture underneath presentations. You’ll in finding vegetable oils in daring.
We’ve gotten hate mail from other people who say sure vegetable oils—particularly cold-pressed canola oil—will have to seem along olive oil within the “devour extra” class. Various others say all vegetable oils belong within the “devour much less” column, and that butter belongs in “devour some” and even “devour extra.”
To know the medical reasoning in the back of our suggestions, let’s discover some head-to-head matchups.
Additional-virgin olive oil vs. expeller-pressed canola oil
Those oils are the least subtle in their sort.
To make further virgin olive oil (EVOO), producers grind and automatically press olives, with out the use of any warmth. In a similar way, expeller-pressed canola oil is made by means of automatically urgent rapeseed, with out using warmth or chemical solvents.
🟢 The case for added virgin olive oil (EVOO)
Olive oil is richer in heart-healthy monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) than virtually some other cooking oil.
As well as, in contrast to the extra subtle “mild” olive oil, EVOO maintains many of the olive fruit’s unique polyphenols. Those plant-based ingredients assist to fight irritation and offer protection to cells from injury.
Possibly most significantly…
Extra research vouch for EVOO’s health-promoting qualities than for some other cooking fats.
For instance, researchers requested 22,892 adults from Southern Italy to self-report their olive oil intake. Individuals who fed on probably the most olive oil (greater than two tablespoons an afternoon) had been 20 p.c much less more likely to die over the 13-year learn about than individuals who fed on the least olive oil (not up to one tablespoon an afternoon).5
Different analysis has related the intake of olive oil with a discounted possibility of:
Top blood pressure6
Middle illness
Kind 2 diabetes7
Dementia8
Cancer9
Intake of olive oil may be related to discounts in LDL ldl cholesterol, particularly when used to exchange saturated fat like butter and coconut oil.10
Smoke level: Must you keep away from cooking with olive oil?
Years in the past, culinary mavens beneficial the use of EVOO most effective on salads and different raw meals. Again then, they assumed EVOO’s somewhat low smoke level (350 to 410F) intended the oil would wreck down when heated, shedding a few of its unique taste and fitness advantages.
We now know that smoke level isn’t as giant a deal as in the past idea.
That’s very true relating to EVOO, whose polyphenols and excessive concentrations of monounsaturated fat assist stay the oil solid when heated.
In analysis that heated a lot of cooking oils to 464 F (240C) after which held them at 356 F (180C) for a number of hours, EVOO remained extra solid than some other oil examined, together with canola oil.11
🟡 The case for expeller-pressed canola oil
Some of the extra reasonably priced cooking oils at the shelf, canola oil, is created from a Canadian-made hybrid of the rapeseed plant.
(The phrase “canola” refers back to the first 3 letters of “Canada” with a amusing “ola” added to the top for advertising and marketing functions.)12
Amongst vegetable oils, canola is the richest in heart-healthy monounsaturated fat (regardless that a number of non-vegetable oils have it beat) in addition to alpha-linolenic acid, a plant-based omega-3 fatty acid.
As well as, canola oil comprises plant ingredients referred to as phytosterols that assist affect blood ldl cholesterol for the easier, particularly when used as an alternative choice to butter, analysis has discovered.13 14 15
The winner
Additional virgin olive oil is the transparent winner.
The frame of analysis in improve of EVOO dwarfs the frame of analysis in improve of expeller-pressed canola.
As well as, EVOO has a extra favorable fatty acid profile. Via the best way, so does avocado oil, which is why you’ll additionally in finding it within the “devour extra” column.
Then again, you’ll be able to purchase kind of two times as a lot expeller-pressed canola oil for part as a lot cash as EVOO. As a result of this, expeller-pressed canola could be a nice budget-friendly selection. As well as, on account of expeller-pressed canola’s extra impartial taste, many of us like it over EVOO for baking.
When utilized in moderation, expeller-pressed canola may also be a part of a nutritious diet. It’s more likely to be a minimum of fitness impartial, if no longer slightly fitness recommended.
Expeller-pressed canola oil vs. subtle canola oil
This match-up comes all the way down to how processing strategies impact the top product.
🟡 Expeller-pressed canola oil
An expeller press is a device that squeezes oil out of seeds.
It’s in a position to do that with out using solvents or warmth, which is helping keep recommended compounds akin to alpha-linolenic acid and phytosterols.
🔴 Subtle canola oil
Refining gets rid of some protecting alpha-linoleic acid whilst including small quantities of dangerous trans fatty acids. This leads to a product this is proportionally decrease in omega-3 fatty acids and better in omega-6 fatty acids.
The winner
Expeller-pressed canola oil wins, however most effective by means of a small margin.
That’s as a result of canola oil begins with a much less arguable fatty acid profile than many different vegetable oils, because the chart underneath presentations. Soybean oil, for instance, has much less heart-healthy monounsaturated fats and a lot more theoretically inflammation-contributing omega-6 fats.

Are omega 6 fatty acids “inflammatory?”
The standard American consumes round 16 to twenty occasions extra omega-6 fat than omega-3s.
This imbalance may just theoretically building up irritation on your frame, doubtlessly elevating your possibility for diabetes, weight problems, and different fitness issues, argue some mavens.16
Years in the past, the advice to stability your omega 6s with omega 3s used to be common. (The prompt “supreme” ratio: Anyplace from 1:1 to 4:1, in want of omega 6s.)
In this day and age, there’s extra debate amongst dietary scientists as as to if this imbalance contributes to persistent irritation, particularly when the ones omega 6s are fed on in entire meals that comprise many different recommended compounds.
For instance, nuts and seeds—each naturally wealthy in omega-6 fat—were related to a spread of fitness advantages, together with discounts in blood ldl cholesterol and irritation.17 18
In 2019, Harvard Well being ran the headline “No need to avoid healthy omega-6 fats.” In improve in their argument, a 2019 learn about from the American Middle Affiliation magazine Movement decided that, if the rest, the intake of omega-6 fat decreased the chance for stroke, coronary heart illness, and early loss of life.19
Then again, whilst nuts and subtle canola oil would possibly percentage a slightly identical fatty acid profile, the 2 meals vary in a single vital manner. As we discussed previous, subtle canola oil is mainly natural oil. In the meantime, nuts and seeds come packaged with health-protective fiber, polyphenols, protein, nutrients, and minerals.
Minimally-processed meals, like nuts or further virgin oils, come with a fancy matrix of health-promoting vitamins. Extremely-processed oils, however, have misplaced nearly all of the ones wholesome compounds, leaving most commonly simply the fatty acids which can be extra at risk of oxidation (we’ll quilt that subsequent).
Subtle vegetable oil oil vs. butter
That is the match-up that triggers probably the most arguing at the interwebs.
Let’s quilt the foremost claims from either side—plus what the analysis says.
🔴 The case for butter
Butter proponents argue that saturated fat were unnecessarily vilified. They level to diet suggestions all through the Eighties and Nineteen Nineties that beneficial folks change butter with trans-fat wealthy margarine.
(Everyone knows how that went.)
Margarine apart, others declare the analysis in improve of lowering saturated fat is skinny at very best.20
Then again, over the top saturated fats intake (past 10 p.c of general energy) does appear to spice up levels of cholesterol and would possibly building up your possibility of coronary heart illness.21
A little analysis has discovered that changing 5 p.c of the saturated fat on your vitamin with monounsaturated fat may just cut back the chance of coronary heart illness by means of 15 p.c. In a similar way, changing 5 p.c of the saturated fat on your vitamin with polyunsaturated fat (with maximum of that coming from subtle vegetable oils) reduces the chance of a long term coronary heart assault by means of 10 p.c, in keeping with an research of 8 research involving 13,614 folks.22 Many different research improve this discovering.23
However no longer all saturated fat impact blood ldl cholesterol similarly. In some dairy meals, a membrane—referred to as a milk fats globule membrane—surrounds the saturated fat and turns out to restrict their cholesterol-raising homes.
Then again, butter is low on this protecting membrane, and as a result raises blood ldl cholesterol greater than different high-fat dairy merchandise, like full-fat milk, cream, yogurt, or cheese.24 25 26
The U.S. Nutritional Tips suggest capping saturated fats at not up to 10 p.c of your calorie consumption. A tablespoon of butter comprises 7 grams of saturated fats—a 3rd of the beneficial day-to-day prohibit in a 2000 Calorie vitamin.
So, whilst you don’t essentially want to get rid of butter, it’s price moderating your consumption.
(Interested by studying about all of the nuances of saturated fats intake? Learn: Is saturated fats nice or unhealthy for you?)
🔴 The case for subtle vegetable oils
Because of their chemical construction, polyunsaturated fat are inherently much less solid and extra at risk of oxidation than saturated or monounsaturated fat.
All the way through the refining procedure, protecting phytochemicals and antioxidants are stripped, making those oils extra at risk of oxidation. The speculation is this oxidation will increase irritation within the frame and elevates the chance of quite a lot of fitness stipulations.
There’s some proof to signify that diets wealthy in polyunsaturated fat, particularly from subtle vegetable oils, are related to greater ranges of oxidized blood lipids, lipid peroxidation, and different markers of irritation.27 28
If you happen to most effective use subtle corn or safflower oils to calmly coat veggies prior to roasting them, you most probably don’t have a lot to fret about.
Then again, for nearly all of folks, the most important supply of subtle vegetable oils isn’t home-cooked foods—it’s ultra-processed meals.
The additional processing and repeated warmth publicity used to create ultra-processed meals additional oxidize those oils. Moreover, those meals are frequently loaded with doubtlessly damaging elements like added sodium and sugars, and occasional in recommended vitamins like fiber, nutrients, minerals, and phytonutrients.
Plus, they’re extremely calorie-dense and tough to forestall consuming, which is able to carry your possibility for weight problems. (To find out precisely why highly-processed meals are so “addictive”: Why you’ll be able to’t prevent consuming ultra-processed meals.)
Maximum ultra-processed meals record a number of vegetable oils as one among their elements. Even ultra-processed meals that you simply wouldn’t recall to mind as “fatty” comprise small quantities. You’ll in finding them in store-bought cookies, chips, crackers, sauces, frozen dinners, meal substitute shakes, boxed macaroni and cheese, salad dressing, boxed rice blends, and extra.
In a big evaluation involving just about 10 million folks, the intake of ultra-processed meals used to be related to a better possibility of untimely loss of life.29 As well as, research have related excessive intake of ultra-processed meals with the next fitness issues:30 31 32 33
Middle illness and coronary heart assaults
Stroke
Hypertension
Despair
Obese and weight problems
Diabetes
Lowered HDL ldl cholesterol
Most cancers
You don’t must abolish ultra-processed meals.
However your fitness will take pleasure in capping your intake to about 20 p.c or so of your consumption, with the opposite 80 p.c or so from most commonly minimally-processed entire meals.
This on my own will naturally decrease your subtle vegetable oil consumption to a more secure degree, with out a lot fuss. Plus, eating subtle vegetable oils within the context of a vitamin that’s wealthy in colourful vegetation, fiber, phytochemicals, and antioxidants would possibly assist offset the fear of oxidation. (For instance, by means of placing an inexpensive quantity of industrial salad dressing on a big, colourful salad.)
The winner
This match-up is a draw.
In the long run, each will have to be restricted within the vitamin, and neither are health-promoting.
Maximum subtle vegetable oils are lopsidedly wealthy in polyunsaturated fatty acids in comparison to monounsaturated fat, and are stripped of many protecting compounds. As discussed previous, some mavens argue that those omega-6-rich fat would possibly give a contribution to irritation (however the proof right here is blended). As a result of how they’re processed, seed oils additionally comprise a few of the ones trans fat that everybody is of the same opinion we will have to all decrease.
By contrast, butter is low in omega 6s however excessive in saturated fats, which may also be problematic in upper quantities. Particularly because it’s so low within the protecting milk fats globule membrane. Then again, in comparison to subtle vegetable oil, butter is much less processed. Like olive oil, it’s a type of fat you should theoretically make at domestic.
Some ultimate parting recommendation
This could be glaring from the head-to-head matchups, however we’ll say it anyway.
If you happen to adore it and will manage to pay for it, EVOO is a smart selection.
Chilly-pressed avocado oil and walnut oil also are nice choices, as each are wealthy in antioxidant compounds. Like EVOO, avocado oil is a wealthy supply of MUFAs. Walnut oil’s fats basically comes from polyunsaturated fat, so it’s very best used as a dressing quite than used for cooking (because it’s much less warmth solid).
Then again, like EVOO, avocado and walnut oil have a tendency to be pricey. If you happen to or your consumer are budget-conscious, expeller-pressed canola oil is a cast runner-up.
In a similar way, high-oleic sunflower and safflower oils are richer assets of monounsaturated fat than their high-linoleic cousins. When substituted for saturated fat like butter, high-oleic oils were related to cardiovascular advantages.34 35
Irrespective of what cooking fat you or your consumer select, you’ll additionally wish to do the next:
✅ Prioritize minimally-processed entire meals.
Entire and minimally-processed meals—akin to nuts, seeds, avocados, olives, and salmon—are much more likely to function health-promoting monounsaturated (MUFAs) and omega-3 fat. Additionally they come packaged with a wide selection of alternative good-for-you vitamins akin to fiber, protein, minerals, and antioxidants.
By contrast, ultra-professed meals are normally devoid of the entirety you stay listening to you will have to eat extra of. Those meals additionally have a tendency to be calorie-dense, extremely rewarding, and difficult to forestall consuming.
If you happen to’re no longer certain whether or not packaged meals is minimally processed or extremely processed, take an in depth glance and believe:
Does the rest in nature resemble this meals?
Does it glance adore it got here from an animal or a plant?
If you happen to take a look at the record of elements, do you notice animal or plant elements?
If you happen to resolution “no” to many of the above, the meals is most probably extremely processed.
✅ Prohibit deep-fried meals.
It doesn’t topic what supply of fats is used to fry them.
Kind all fried meals into the “devour much less” class.
✅ Get maximum of your fat from meals, no longer oils.
EVOO is related to longer, more fit lives. Then again, that doesn’t imply you will have to be doing photographs of it.
As a normal rule, you’re getting maximum of your fats from meals like avocados, olives, nuts and seeds than from any cooking oil.
Entire meals fat are wealthy in fiber, phytochemicals, nutrients, and minerals, and are normally much less calorie-dense than oils. (However having one to 3 servings of oils or butter consistent with day is affordable.)
And if you need personalised recommendation to fit your frame, your consuming personal tastes, and your targets, take a look at our Diet Calculator to determine how fat are compatible into your total vitamin.
References
Click on right here to view the tips assets referenced on this article.
N.d. Accessed January 14, 2025. https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/1103679/nutrients.
N.d. Accessed January 14, 2025. https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/169998/nutrients.
Heart for Meals Protection, and Carried out Diet. 2024. “Trans Fats.” U.S. Meals and Drug Management. FDA. April 30, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/food/food-additives-petitions/trans-fat.
Szabo, Zoltan, Tamas Marosvölgyi, Eva Szabo, Viktor Koczka, Zsofia Verzar, Maria Figler, and Tamas Decsi. 2022. Effects of Repeated Heating on Fatty Acid Composition of Plant-Based Cooking Oils. Meals (Basel, Switzerland) 11 (2): 192.
Ruggiero, Emilia, Augusto Di Castelnuovo, Simona Costanzo, Simona Esposito, Amalia De Curtis, Mariarosaria Persichillo, Chiara Cerletti, et al. 2024. Olive Oil Consumption Is Associated with Lower Cancer, Cardiovascular and All-Cause Mortality among Italian Adults: Prospective Results from the Moli-Sani Study and Analysis of Potential Biological Mechanisms. Eu Magazine of Medical Diet 78 (8): 684–93.
Ferrara, L. A., A. S. Raimondi, L. d’Episcopo, L. Guida, A. Dello Russo, and T. Marotta. 2000. Olive Oil and Reduced Need for Antihypertensive Medications. Archives of Inside Drugs 160 (6): 837–42.
Martínez-González, Miguel A., Carmen Sayón-Orea, Vanessa Bullón-Vela, Maira Bes-Rastrollo, Fernando Rodríguez-Artalejo, María José Yusta-Boyo, and Marta García-Solano. 2022. Effect of Olive Oil Consumption on Cardiovascular Disease, Cancer, Type 2 Diabetes, and All-Cause Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medical Diet (Edinburgh, Scotland) 41 (12): 2659–82.
Tessier, Anne-Julie, Marianna Cortese, Changzheng Yuan, Kjetil Bjornevik, Alberto Ascherio, Daniel D. Wang, Jorge E. Chavarro, et al. 2024. Consumption of Olive Oil and Diet Quality and Risk of Dementia-Related Death. JAMA Community Open 7 (5): e2410021.
Markellos, Christos, Maria-Eleni Ourailidou, Maria Gavriatopoulou, Panagiotis Halvatsiotis, Theodoros N. Sergentanis, and Theodora Psaltopoulou. 2022. Olive Oil Intake and Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PloS One 17 (1): e0261649.
Teng, Kim-Tiu, Radhika Loganathan, Boon How Chunk, and Tsung Fei Khang. 2024. Diverse Impacts of Red Palm Olein, Extra Virgin Coconut Oil and Extra Virgin Olive Oil on Cardiometabolic Risk Markers in Individuals with Central Obesity: A Randomised Trial. Eu Magazine of Diet 63 (4): 1225–39.
De Alzaa, F., C. Guillaume, and L. Ravetti. 2018. Evaluation of Chemical and Physical Changes in Different Commercial Oils during Heating. Acta Clinical Dietary Well being 2 (6): 02–11.
Hollandbeck, Andy. 2020. “In a Phrase: The Introduction of Canola Oil.” The Saturday Night Put up. November 12, 2020. https://www.saturdayeveningpost.com/2020/11/in-a-word-the-creation-of-canola-oil/.
Pourrajab, Behnaz, Elham Sharifi-Zahabi, Sepideh Soltani, Hossein Shahinfar, and Farzad Shidfar. 2023. Comparison of Canola Oil and Olive Oil Consumption on the Serum Lipid Profile in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Vital Evaluations in Meals Science and Diet 63 (33): 12270–84.
Morgan, S. A., A. J. Sinclair, and Okay. O’Dea. 1993. Effect on Serum Lipids of Addition of Safflower Oil or Olive Oil to Very-Low-Fat Diets Rich in Lean Beef. Magazine of the American Dietetic Affiliation 93 (6): 644–48.
Pourrajab, Behnaz, Elham Sharifi-Zahabi, Sepideh Soltani, Hossein Shahinfar, and Farzad Shidfar. 2023. Comparison of Canola Oil and Olive Oil Consumption on the Serum Lipid Profile in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Vital Evaluations in Meals Science and Diet 63 (33): 12270–84.
Shetty, Shilpa S., N. Suchetha Kumari, and Remya Varadarajan. 2023. The Ratio of Omega-6/Omega-3 Fatty Acid: Implications and Application as a Marker to Diabetes. In Biomarkers in Diabetes, 449–67. Cham: Springer World Publishing.
Guasch-Ferré, Marta, Jun Li, Frank B. Hu, Jordi Salas-Salvadó, and Deirdre Okay. Tobias. 2018. Effects of Walnut Consumption on Blood Lipids and Other Cardiovascular Risk Factors: An Updated Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Controlled Trials. The American Magazine of Medical Diet 108 (1): 174–87.
Yu, Zhi, Vasanti S. Malik, Nana Keum, Frank B. Hu, Edward L. Giovannucci, Meir J. Stampfer, Walter C. Willett, Charles S. Fuchs, and Ying Bao. 2016. Associations between Nut Consumption and Inflammatory Biomarkers. The American Magazine of Medical Diet 104 (3): 722–28.
Marklund, Matti, Jason H. Y. Wu, Fumiaki Imamura, Liana C. Del Gobbo, Amanda Fretts, Janette de Goede, Peilin Shi, et al. 2019. Biomarkers of Dietary Omega-6 Fatty Acids and Incident Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality: An Individual-Level Pooled Analysis of 30 Cohort Studies. Movement 139 (21): 2422–36.
Krauss, Ronald M., and Penny M. Kris-Etherton. 2020. Public Health Guidelines Should Recommend Reducing Saturated Fat Consumption as Much as Possible: NO. The American Magazine of Medical Diet 112 (1): 19–24.
American citizens, For. n.d. “Lower Down On.” Accessed January 14, 2025. https://odphp.health.gov/sites/default/files/2019-10/DGA_Cut-Down-On-Saturated-Fats.pdf.
Mozaffarian, Dariush, Renata Micha, and Sarah Wallace. 2010. Effects on Coronary Heart Disease of Increasing Polyunsaturated Fat in Place of Saturated Fat: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. PLoS Drugs 7 (3): e1000252.
Kris-Etherton, Penny M., and Ronald M. Krauss. 2020. Public Health Guidelines Should Recommend Reducing Saturated Fat Consumption as Much as Possible: YES. The American Magazine of Medical Diet 112 (1): 13–18.
Kanon, Alexander P., Sarah J. Spies, Alastair Okay. H. MacGibbon, and Maher Fuad. 2024. Milk Fat Globule Membrane Is Associated with Lower Blood Lipid Levels in Adults: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Meals (Basel, Switzerland) 13 (17): 2725.
Pan, Junyu, Meiqing Chen, Ning Li, Rongwei Han, Yongxin Yang, Nan Zheng, Shengguo Zhao, and Yangdong Zhang. 2023. Bioactive Functions of Lipids in the Milk Fat Globule Membrane: A Comprehensive Review. Meals (Basel, Switzerland) 12 (20). https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12203755.
Rosqvist, Fredrik, Annika Smedman, Helena Lindmark-Månsson, Marie Paulsson, Paul Petrus, Sara Straniero, Mats Rudling, Ingrid Dahlman, and Ulf Risérus. 2015. Potential Role of Milk Fat Globule Membrane in Modulating Plasma Lipoproteins, Gene Expression, and Cholesterol Metabolism in Humans: A Randomized Study. The American Magazine of Medical Diet 102 (1): 20–30.
Choe, Eunok, and David B. Min. 2006. Mechanisms and Factors for Edible Oil Oxidation. Complete Evaluations in Meals Science and Meals Protection 5 (4): 169–86.
DiNicolantonio, James J., and James H. O’Keefe. 2018. Omega-6 Vegetable Oils as a Driver of Coronary Heart Disease: The Oxidized Linoleic Acid Hypothesis. Open Middle 5 (2): e000898.
Lane, Melissa M., Elizabeth Gamage, Shutong Du, Deborah N. Ashtree, Amelia J. McGuinness, Sarah Gauci, Phillip Baker, et al. 2024. Ultra-Processed Food Exposure and Adverse Health Outcomes: Umbrella Review of Epidemiological Meta-Analyses. BMJ 384 (February): e077310.
Pagliai G, Dinu M, Madarena MP, Bonaccio M, Iacoviello L, Sofi F. Consumption of ultra-processed foods and health status: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Nutr. 2021 Feb 14;125;3:308–18.
Srour B, Fezeu LK, Kesse-Guyot E, Allès B, Méjean C, Andrianasolo RM, et al. Ultra-processed food intake and risk of cardiovascular disease: prospective cohort study (NutriNet-Santé). BMJ. 2019 Might 29;365:l1451.
Mendonça R de D, Lopes ACS, Pimenta AM, Gea A, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Bes-Rastrollo M. Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and the Incidence of Hypertension in a Mediterranean Cohort: The Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra Project. Am J Hypertens. 2017 Apr 1;30(4):358–66.
Cordova R, Viallon V, Fontvieille E, Peruchet-Noray L, Jansana A, Wagner KH, et al. Consumption of ultra-processed foods and risk of multimorbidity of cancer and cardiometabolic diseases: a multinational cohort study. Lancet Reg Well being Eur. 2023 Dec;35:100771.
Shramko, Viktoriya S., Yana V. Polonskaya, Elena V. Kashtanova, Ekaterina M. Stakhneva, and Yuliya I. Ragino. 2020. The Short Overview on the Relevance of Fatty Acids for Human Cardiovascular Disorders. Biomolecules 10 (8): 1127.
Human Meals Program. 2024. “FDA Completes Assessment of Certified Well being Declare Petition for Oleic Acid and the Chance of Coronary Middle Illness.” U.S. Meals and Drug Management. FDA. September 3, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/food/cfsan-constituent-updates/fda-completes-review-qualified-health-claim-petition-oleic-acid-and-risk-coronary-heart-disease.
If you happen to’re a trainer, or you need to be…
You’ll assist folks construct sustainable diet and way of life conduct that can considerably strengthen their bodily and psychological fitness—whilst you’re making a really perfect residing doing what you’re keen on. We will display you ways.
If you happen to’d like to be told extra, believe the PN Stage 1 Diet Training Certification. (You’ll join now at a large cut price.)